What is CRM?
CRM (Customer Relationship Management), is an acronym derived from its full name, as the name implies, is a strategy used by businesses to maximize sales revenue and improve customer retention by developing and maintaining customer relationships. The advantage of CRM lies in its ability to provide clear visibility into the customer journey and sales process, thereby ensuring that team members are on the same page based on the latest information.
In the modern business environment, the term CRM is often followed by words like “systems”, “platforms”, or “tools”. In short, CRM tools is an integrated platform that consolidates various interactions from sales, customer support, and marketing, providing a comprehensive view of the business and becoming an indispensable tool for enterprises.
The world of CRM is vast, and this article will delve into what a CRM system is: the different types of CRM systems driven by various objectives, the core roles within a CRM system, and its functional applications. We will also explore the benefits of using a CRM system and how it can help enterprises achieve growth across various departments.
B2B and B2C CRM: Have You Found the Right CRM?
Although both B2B and B2C CRM systems aim to strengthen customer relationships, due to their fundamental differences in transaction objects, sales processes and customer interaction methods, the functional focus and application methods of the systems are also different.

B2B CRM (Business-to-Business Customer Relationship Management)
The CRM system for B2B focuses on project-centric relationships, emphasizing the deepening of business relations and fostering long-term cooperation between companies. Here are its core features:
- Sales Stage Tracking:
B2B transactions usually involve multiple pre-sale stages of pitching and interaction, with complex and lengthy decision-making processes that require customized solutions and quotations for different customer needs. CRM systems need to provide robust progress tracking to monitor each stage of the business transaction, allowing businesses to precisely manage the progress of each deal, handle these custom requests flexibly, and maintain accuracy and consistency, ensuring that every link in the sales funnel is properly managed. - Consistent Internal Communication:
Business purchasing decisions often involve multiple departments or team members interacting with clients. In sales processes with multiple participants, CRM systems can facilitate collaboration among colleagues, ensure information sharing, and prevent business conflicts. By instantly viewing information at every stage of the transaction, the team can have a unified understanding of the client’s status and needs, resulting in effective communication and consistent proposal delivery.
B2C CRM (Business-to-Consumer Customer Relationship Management)
B2C CRM systems focus on visualizing insights from large volumes of consumer data to achieve a high level of market analysis; subsequently, using the interactive functions within the CRM system for automation and personalized marketing. Key features include:
- Integration of Customer Data Across Various Channels:
B2C companies often manage data for thousands of customers. Consumers are more likely to interact with a company through more than one channel, and even a single consumer may have diverse sources of information. Their CRM systems must be capable of handling large volumes of data and quickly and accurately identifying and categorizing customer information. In addition, B2C CRM systems must integrate customer data from offline stores, online shops, social media, email, and other channels, to form a unified customer view. - Targeted Marketing Using Analytical Results:
As consumer groups are large and varied, effective targeted marketing requires CRM systems to digest insights from consumer behavior, preferences, and purchase history to achieve high-level market analysis. Then, based on these results, segment them into different groups to provide more precise personalized services. - Automation of Personalized Marketing:
Since consumers often seek a personalized shopping experience, B2C companies usually engage in large-scale personalized marketing campaigns. CRM systems should support these targeted marketing activities and be capable of automation. They should be able to generate personalized marketing messages in bulk automatically, based on customers’ historical transactions and interaction data, enabling personalized interactions through computer systems and ensuring communication with customers is more targeted and tailored to individual needs.
The Importance of Choosing the Right CRM
Imagine a retail business with a B2C orientation; if it chooses a CRM system with a tendency towards B2B functionalities, no matter how powerful the B2B features of that system are, without automation or customer interaction marketing capabilities, it amounts to nothing more than an elaborate customer database for the B2C business.
If a CRM system that does not fit the business needs of the company is mistakenly chosen in the planning stage, not only will the desired results not be achieved, but also a significant amount of development time and human resources will have been wasted before the problem is identified.
Only the businesses who can maximize the effectiveness of its customer relationship management strategy by wisely selecting a CRM system that suits its business model
The Core Role of B2C CRM Systems in Retail Businesses
B2C CRM systems encompass automated processes that liberate teams from the burdens of marketing, sales, and customer support tasks. Through a centralized dashboard, all tasks and data can be filtered, managed, and kept in one place. This centralization allows various departments to easily view and share up-to-date information and to customize and integrate it according to the specific needs of the organization.
CRM systems are capable of storing essential information such as contact methods, behavioral records, purchasing behavior, and communication preferences, and they can also use this data to prioritize business opportunities, automatically schedule interactions with potential customers, and record every interaction—even those that do not lead to sales. This means that sales representatives do not have to manually enter data and can also gain a wealth of useful information, thereby creating personalized experiences for future communications.
CRM systems enable even teams that lack organized management to track all customer data throughout the entire customer journey, allowing for timely corrections at any stage of the customer lifecycle to prevent churn. By collecting, storing, and analyzing key customer data, such as purchase history, behavioral patterns, and personal preferences, customer service personnel can better understand how to engage customers and increase satisfaction.
Seamless O2O Customer Journeys: CRM & Loyalty Platform
To learn more about our powerful O2O-centric CRM & Loyalty Platform, visit our page and discover the advantages of seamless O2O customer journeys and real-time interaction capabilities!
Why Are CRM Systems Important? How They Help Businesses Grow
In today’s competitive market, understanding customers and building long-term relationships is key to success. CRM systems offer a comprehensive platform that helps businesses collect various kinds of data on customer interactions, enabling them to provide personalized services or products, increase sales, and enhance the quality of customer service.
CRM systems drive sales strategies, marketing campaigns, and customer service processes by integrating customer data. Businesses can use this data for targeted marketing, predicting sales trends, and providing excellent customer service, which can increase revenue and reduce costs.
Advantages of Using a CRM System

1. Enhanced Customer Experience and Satisfaction
- Personalized Service: Use CRM to record specific customer interactions for personalized responses.
- Instant Response: Respond to customer needs quickly with real-time communication and automation tools.
- Consistent Communication: Ensure all customer communications are consistent to improve interaction quality.
- Optimized Customer Experience: Design marketing campaigns based on customer behavior and preferences to increase engagement.
CRM systems provide a complete customer database, enabling businesses to track every interaction and preference. This insight allows them to deliver highly personalized service, thereby enhancing the customer experience. For example, customer service teams can view a customer’s purchase history and previous communications before contact, allowing for more targeted responses. Automation features in CRM can help reply to customer queries promptly, reducing wait times and increasing satisfaction.
2. Improved Work Efficiency and Process Automation
- Automated Processes: Reduce manual entry and automatically execute routine tasks like email sending.
- Time Savings: Automation frees up staff time to focus on more valuable work.
Automation is one of the key features of CRM systems. It can handle many tedious daily tasks, such as scheduling emails, updating sales opportunity statuses, and generating reports. This not only helps reduce human errors but also allows sales and customer service teams to focus their time and energy on more complex and valuable tasks, thereby improving overall work efficiency.
3. Data-Driven Goal Setting and Progress Tracking
- Clear Goals: Use CRM tools to set sales and service goals.
- Progress Visualization: Track progress in real time and adjust strategies to ensure goals are met.
CRM tools help businesses set specific sales goals and corresponding timelines. Visual progress tracking allows management to easily monitor team progress and adjust strategies timely to ensure goal attainment. This data-driven approach provides clear direction and motivation, promoting teamwork and performance improvement.
4. Sales Growth and Customer Retention
- Identifying Sales Opportunities: Analyze customer data to improve conversion rates.
- Retention Strategies: Predict customer churn risk and take action through analysis.
By analyzing customer data, CRM systems can help sales teams identify opportunities for cross-selling and upselling, increasing conversion rates and sales. Additionally, CRM can help businesses predict and prevent customer churn by identifying dissatisfied customers early and taking proactive measures to improve their experience, thereby increasing retention rates.
5. Integrated Data and In-Depth Analysis
- Comprehensive Data Integration: Manage and analyze information from various channels centrally.
- Accurate Forecasting: Make sales predictions and business analysis based on data.
CRM systems can integrate customer data from different channels, including social media, emails, phone calls, and physical storefronts. This integration provides a 360-degree view of the customer and allows for in-depth business analysis based on comprehensive data. This analysis can guide decision-making, enhance products and services, and make sales forecasting more accurate. Using a data-driven approach, businesses can better understand market trends, customer behavior, and predict future business opportunities or potential risks, thereby devising more effective business strategies.
6. Targeted Marketing and Campaign Evaluation
- Targeted Marketing: Carry out customized marketing campaigns based on customer segmentation.
- Campaign Analysis: Measure the effectiveness of marketing campaigns and adjust based on feedback.
Another key function of CRM systems is helping businesses conduct more precise marketing campaigns. By deeply analyzing customer data, businesses can create well-defined customer segments and launch tailored marketing campaigns for those networks. This not only improves the relevance and appeal of marketing efforts but also enhances ROI. The analytical tools provided by CRM systems help businesses measure the effectiveness of various marketing activities and optimize and adjust based on this data, achieving the best marketing outcomes.
Boost Loyalty Rewards Program with Personalized White Label App
To learn more about boosting your loyalty rewards program with a personalized white label app, visit our page and experience the full-featured loyalty app with personalized offers and a multiple owned channels approach!
Examples of CRM System Functional Applications
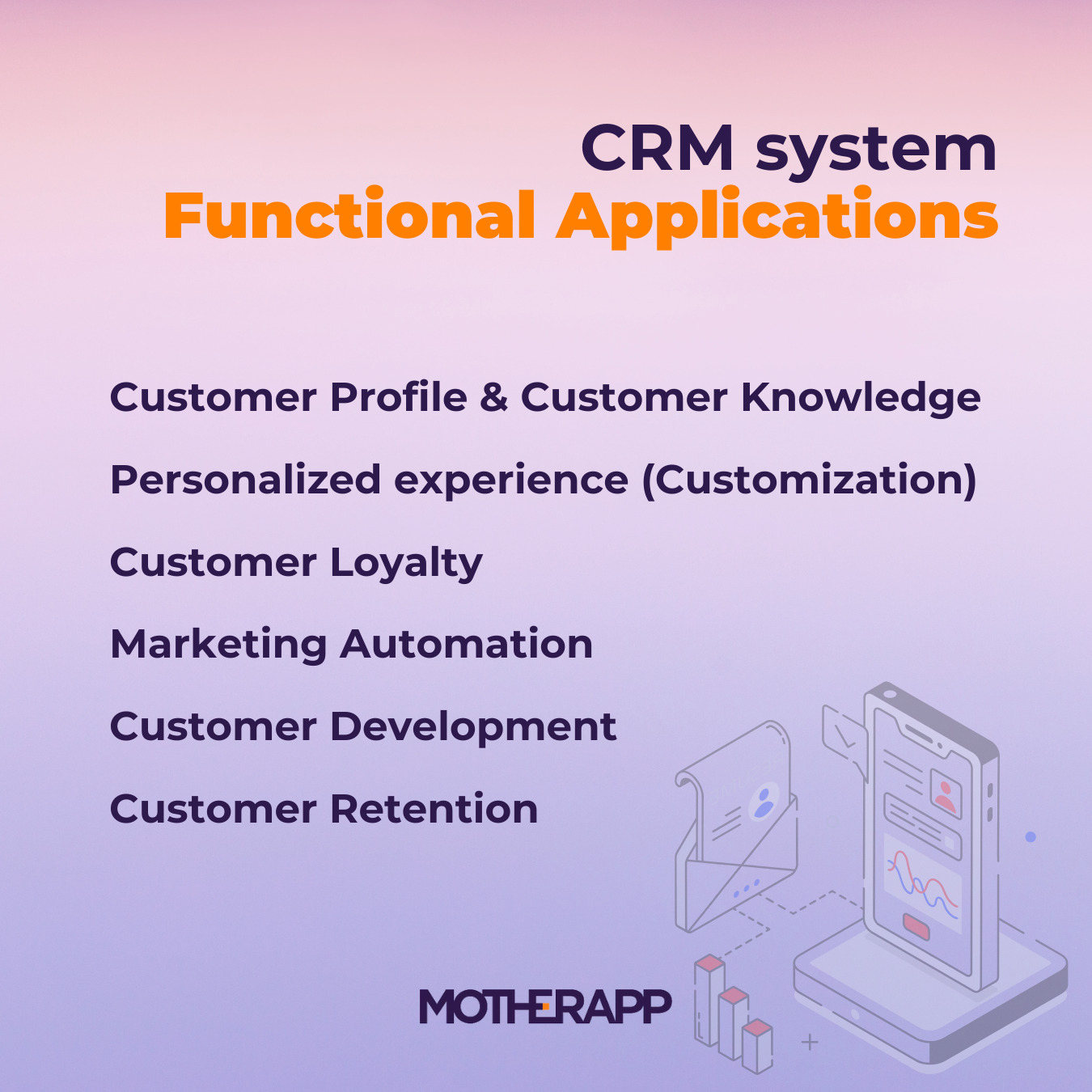
Both B2B and B2C CRM systems aim to strengthen customer relationships. No matter the type of CRM, they can encompass a variety of functions applied within the broad scope of customer relationship management. They play a vital role in helping retailers acquire new customers, maintain existing customer relationships, enhance customer satisfaction, and improve overall sales performance. Additionally, they foster customer loyalty. We have selected a few key function applications of CRM systems to exemplify:
Customer Database Management (Customer Profile & Customer Knowledge):
A CRM system’s customer database management feature is all about storing and organizing customer info across different platforms, like contact details, POS transaction histories, communication logs, and customer feedback. Centralizing this data makes it super easy for businesses to grab customer info fast and keep it up-to-date.
Example:
An e-commerce company uses its CRM to manage a huge customer database. Whenever customers shop, the system automatically records their purchases and saves their personal info and payment methods. Plus, when customers reach out through various channels like phone, email, or social media, the CRM makes sure these inquiries are logged and sent to the right customer service rep. This way, when a customer contacts them again, the service team can pull up past interactions and offer personalized help and solutions on the spot.
Customization (Personalized Experience):
By digging into customer data, CRMs help retailers create a shopping experience that feels tailor-made for each customer.
Example:
A bookstore tracks customers’ reading tastes and habits through its CRM, then uses that info to offer personalized recommendations. When new books drop or related events pop up, the bookstore can send custom alerts to customers who’d be into that sort of thing. This kind of personal attention not only makes customers more loyal but also boosts sales.
Customer Loyalty:
CRM’s loyalty features help businesses build long-term customer relationships by offering rewards programs, exclusive member events, or regular customer experience surveys to increase loyalty and retention.
Example:
A coffee chain uses its CRM to run a member rewards program. Every purchase racks up points that customers can swap for free drinks or other perks. The CRM also sends personalized coupons to regulars as a thanks for their loyalty. These moves significantly up the chances of customers coming back and sticking with the brand.
Marketing Automation:
CRMs’ marketing automation tools let retailers run marketing campaigns that draw in more customers and up sales. This often involves automated tools for email marketing, social media ads, and lead scoring and tracking to manage and refine the effectiveness of marketing efforts.
Example:
Retailers can use CRM marketing automation tools to design and implement email marketing campaigns. The system can send personalized product recommendations and promotions based on a customer’s purchase history and browsing behavior, nudging them toward a purchase. These tools can also automate notifications for holiday sales and adjust future marketing strategies based on customer interactions to boost conversion rates.
Customer Development:
CRMs allow retailers to increase customer value through cross-selling and upselling strategies, suggesting products or services that customers might be interested in.
Example:
An electronics store uses its CRM to track customer behavior after they buy big-ticket appliances. The system notices these customers often look for related small appliances or accessories. So, the store starts recommending these related products to customers after they buy a major appliance.
Customer Retention:
The retention features in a CRM help businesses predict the risk of customers churning by deeply analyzing customer data and taking steps to prevent it. This might include tailored marketing campaigns for specific customer groups, sending out coupons, or offering personalized services.
Example:
A mobile carrier uses its CRM to analyze customer usage data and identify those at high risk of switching to competitors. Then, the company offers special renewal deals or add-on services to encourage these customers to stay.
Customizable Loyalty Platform for Business Needs: Tailored to Your Brand
Unlock the true potential of your brand with our customizable loyalty platform tailored to your business needs. Visit our page and discover seamless integration, tailor-made apps, and battle-tested security for your brand’s success!
Cross-Departmental Applications of CRM Systems
In a company, CRM systems can be used across different departments. They’re not just about boosting internal operational efficiency; they also play a key role in increasing customer satisfaction and loyalty. Let’s check out a few examples of how they’re used:
Sales Department
The sales team can tap into the CRM to track customers’ buying history and preferences, so they can recommend products or services more accurately. For instance, if the CRM notes that a customer often picks up new sneakers in the fall, the sales crew can hit them up as the season changes to promote the latest sneaker drops.
Customer Service Department
Customer service reps use the CRM to manage records of customer interactions, providing more personalized service. Like, when a customer calls in with a product question, the service agent can quickly pull up their purchase and interaction history to give tailored answers and support.
Marketing Department
The marketing squad uses the CRM for segmenting the market and pinpointing target customers, making their campaigns way more effective. For example, by analyzing data with the CRM, marketers can spot the customer groups most likely to vibe with certain promos, and then send out customized emails or social media ads just for them.
Inventory Management Department
Inventory managers can use the CRM’s data analysis features to predict demand trends for specific products, helping them manage stock levels like a boss. Say the data suggests an uptick in sales of a product line each quarter; inventory can adjust their orders in advance to make sure they’ve got just enough stock without going overboard.
These articles might interest you
【CRM Trends】Doing Good with Points: Members Point Donation
Seize Customers Through Direct Membership Program | Direct-to-Consumer (D2C) Retail Strategies
Advanced Marketing Approach – ABC Marketing
Stop Guessing Preferences: Data-Driven Marketing
New Privacy Trend III: O2O to OMO Platform Ownership
Further case study explorations
Carbon Wallet – Different Use of Loyalty Program
Carbon Wallet Rebranding a Green Lifestyle Community
Link Up – Linking Daily Life with Link Shopping Mall App
Francfranc FUN! – Loyalty Program for Affordable Luxury
Contact us now for more professional advice and one-on-one consultation.
Keep up with us – follow us on social media!